Environmental Management and Sustainable Development in India The Concern
The concern about rising environmental problems is universal. The crucial role of people and policies in safeguarding the global environment is sufficiently understood. However, the effective action has been lacking and inadequate. International conferences and programmes since the beginning of seventies have helped environmental thinking and planning but the results are not always directly proportionate.
In India the resources are not always put to optimum use. There is always a wide gap between policy and practice. This lack of direction is due to the multidisciplinary nature of environmental management. For which the individuals and institutions, including the government, the regulator, had not been equipped with.
Our forests are vanishing, soil is eroding. Wild life is retreating and rivers are thinning due to deficiency of rains in general. The environment is becoming less inhabitable. It seems we are approaching to a slow-motion death. There is an explosion of population, both humans and livestock. A suitable action for sustainable development is the need of the hour.
It is the universal truth that economic development takes place on the natural resources base. On the same side, depreciation of natural resources is unavoidable. We must take necessary steps right now. We are the sixth largest tropical forest country. We are facing boundless threat of deforestation.
Pressures of Development on Ecology
Water and soil are also facing various forms of pressures. We forcefully argue that due to local development, be it the rural development or urban development, inevitably influenced by the global development, shall not deplete or adversely affect the balance of our ecology. Violation of ecological principles by humans equates the violation of ethical code of conduct. Hence for our safe future, environment management and development shall go together. We all share our single environment system. So, its safety is our utmost responsibility. Without it, our life is not sustainable.
Land is the place of our development. Our rural population live and work in proximity with nature. They love and worship nature in one form or the other. Intensification of use of resources and diversify of our occupation have certainly serious challenges to balance economic growth in India. Villagers are facing the need of food and fuel along with facing fast encroaching urbanization on the other hand. However, both have disastrous consequences on nature.
Modern development in urban areas has resulted in stress and strain while in the rural, it has brought distress and drain of resources. It needs a thorough study of strengths and weaknesses along with opportunities and threats for economic development. This will create the awareness for the prioritization of economic activities in the country to make best us of the available resources.
Keeping in mind the above factors, the study of sustainable methods of environmental management and the general approach with multidisciplinary involvement at different levels for management of sustainable development is needed to draw the attention of all stakeholders i.e. the policy makers, rural and urban population for resource management.
Conceptual and Practical Issues of Environmental Management and Economic Development in India
Ecological modernization is the dominant concept of sustainable development within the developing countries and as recently seen in some of the sustainable development policy documents of such countries. What is the dominant and important in these policy documents is the consensus for taking up the task of environment management in the respective countries, not merely for the sake of sustainable development but also for the sake of the economic security of the people.
The assimilation of sustainable development and economic security in India is found more loudly among the supporters of sustainable development. However, a purely economic analysis of the sustainable development has been weak. Whenever, a voice is heard regarding sustainability, it has been on natural catastrophes or as a critic of socio-economic failures of capitalism, or its modern face, globalism.
The sustained effort for meeting the challenges of sustainable development is always missing. Also is missing the point of evolvement for eco-efficiency of the factors for production in our political as well as economic policies. Efforts are being made recently to fill the gap of sustainable thinking by several environmentalists, activists, and thinkers.
They have proposed some models of green political economy to outline sustainable development as well as to chalk out some action plans eminently stressing for political aims, principles, and objectives. However, we need to go beyond to produce what is ideal as well as practical. It is necessary to be taken for inter-disciplinary effort to think at bottom line through the political economy of sustainable development.
We know that in India, the earliest civilizations grew and prosperous in a natural habitat. They cultivate the reverence for the mother nature. Hence, the need of the hour is the combination of practicality and extremism for the starting point for policies to create an atmosphere for sustainable development.
We must begin from where we are, with the existing structures, modes of production, institutions, and regulations or so on what practically, we have at present. At the same time, we must be ready and prepared for change and reforms. Ands for abandoning such which is not needed, is unnecessary or to the most, is harmful for the maintenance of sustainable development economy as well as society.
We must work through these existing structures to ensure successful management of environment for balanced economic development. Hence it is clear that the concept of progress as well as development journey of a nation is undoubtedly dependent on its own resources, which we term as environment. The matter is not just use it but also to conserve it for overall productivity.
What is maintainable and repairable in India is, natural resources needs to be managed while the unreplaceable resources, such as biodiversity needs to be conserved. Hence, our common concern over the availability of natural resources and environmental consequences of resource exploitation has given a new height to the relationship between human and nature.
This relationship makes us understand that economic development is not only growth and change in systems but managing the growth and change. The spirit of this approach and its consequences on poverty eradication lies in reconciling human needs and the environment’s capacity to manage with the consequences of the systems. This approach is called sustainable development.
The Sustainable Development, We Mean
For environment, sustainable development is interpreted to mean that individuals care for the environment they live in for their good. It is to refrain from doing anything that is bad and would cause irreparable damage to this biological capital, for now nor in future. Sustainable development in its broadest sense includes developing the potential uses of environment while making humans capable to manage the health of the environment. It strikes a balance between interest as well as benefits, between economic growth and protection of environment.
Hence, the main characteristic of sustainable development is to improve human quality of life within supporting eco-systems, achieving economic growth without destroying our limited resources, promoting development that protects and increases our natural environment and fair use of environment and empowerment of people and society at large.
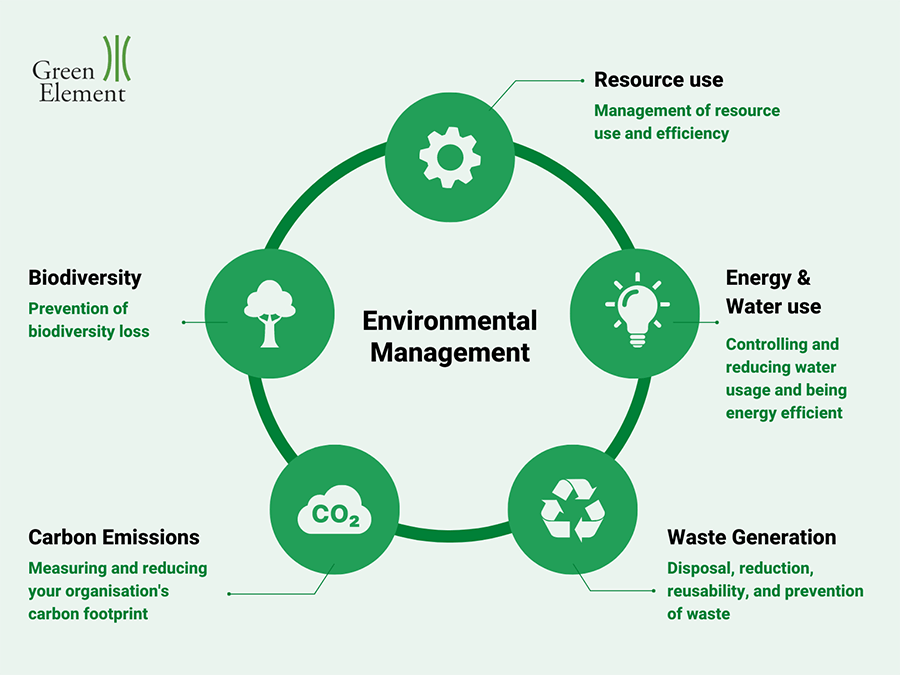
Now the question arises, what is the need of management of assets of biological capital. At the same time what is its management. How can the assets of biological capital be maintained, even increased without adversely effecting others. These are the core questions for the study of management of natural resources and making the different stakeholders aware of it. Environment management must include soil conservation, land reclamation, management of water resources and forests, protections of animals and birds, prevention of atmospheric pollution and waste management.
The Relationship of Natural Resources and Economic Development
The issue of use as well as misuse of natural resources by human beings is ultimately connected with economic development. India is rich with natural resources and healthy natural surroundings. We all living beings are dependent on our natural surroundings. That is why human occupations called human activities are carried on this surface of earth. Therefore, the rate, course and possibility of economic development are determined by the existence and use of the natural resources.
The major resources of this earth are land, water, air and forests and every country, rich or poor, must take care of these. The principle is that the use of natural resources must be optimum, on short or on long run. It is not for the national or international regulations and agreements, but it must be an individuals’ commitment.
The developed countries use more resources than the poor and developing nations. They have greater equalities of wealth distribution. Therefore, the glaring inequalities in wealth consumption in India is quite a challenge that how can our country maintain economic growth alongside environment management.
At the same time, we ought to attain faster growth without degrading the environment. The ecological imbalance has come from both the sides. Both, development, and environment, must address the challenge. With new incentives and implications of liberal and global approach in economic growth, these issues tend to become more complicated.
This is true for India.